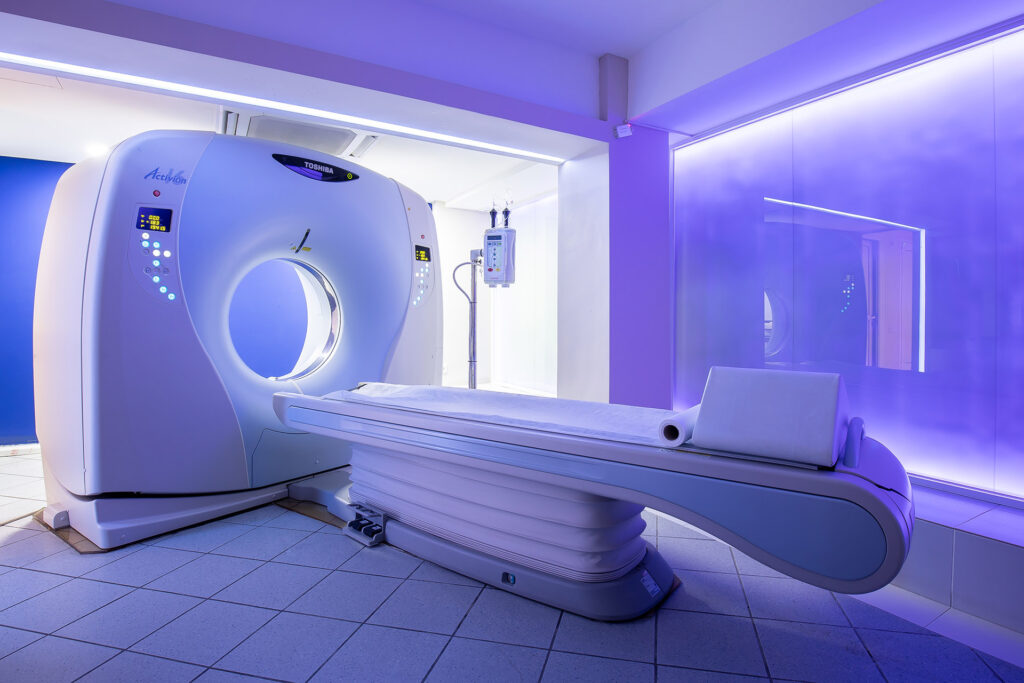
The following CT scans are performed at our center:
- CT scan
- Visceral Cranial Computed Tomography
- Computed Tomography of Lithoid bones
- CT scan of the neck
- Thoracic computed tomography
- Computed Tomography Upper - Lower Abdomen
- CT scan of the retroperitoneal space
- Computed Tomography of the Upper and Lower Extremities
- CT Scan of the Spine (Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar)
- Computed Tomography of Pelvis - Hips
- CT scan of the ankle joint (TAJ), Extremity Foot
- Computed Tomography of the Carpal Joint (PCG), Hand Extremity
- Computed tomography of the eye sockets
- CT Scan of the Jaw (DentalScan)
- Three-dimensional image reconstruction (3D imaging)
AXIAL ANGIOGRAPHY AND SPECIAL PROTOCOLS
Special sketching protocols are performed at our center.
Axial angiography of the carotid and vertebral-basal system.
Axial brain angiography.
Axial angiography of the thoracic and abdominal aorta.
Axial angiography of iliac arteries and lower extremity arteries.
Axial angiography of the upper extremities
Pulmonary Artery CT Angiography (pulmonary embolism protocol)
Protocols for investigation of liver, bile ducts, pancreas, kidneys, adrenal glands as well as CT urography.
It is important that the examinee informs the staff of any known allergies prior to the examination that will be performed with intravenous contrast.
What is a CT Scan?
Computed Tomography (CT) is an imaging technique that
uses ionizing radiation to visualize the internals in detail
body structures.
How does the CT scanner work?
The CT scanner consists of an x-ray producing lamp which
produces a thin beam of radiation. The x-ray lamp rotates around
from the patient's body and thin transverse sections are taken in the area
of interest (perpendicular to the central axis of the patient), thus allowing the
two-dimensional and three-dimensional visualization of body structures. Since the radiation
penetrates the patient's body, hits the detectors and then with the
with the help of electronic devices and specialized software, the digital is created
image. This image is displayed on appropriate diagnostic screens in order to
get an opinion from the medical Radiologist. The image is saved on a CD and given
to the patient along with the opinion.
In what cases is a CT scan used?
Computed tomography is a very useful tool for diagnosis and
characterization of various diseases. More specifically, it is used for:
• The diagnosis of respiratory, gastrointestinal,
biliary and nervous system
• The diagnosis of injuries, craniocerebral injuries, fractures, muscle
bleeding disorders
• Locating the location and size as well as its characterization
formation of tumors
• The study of blood vessels (CT angiography)
• In the study of the urinary system (axial pyelography - axial
urography)
• Imaging guidance of percutaneous punctures such as biopsies,
and
• Monitoring the effectiveness of treatments such as
chemotherapy in oncological patients.
With modern CT systems, an examination is performed on
just a few minutes.
Use of contrast agent
In order to create contrast (for better visualization) between an instrument
and adjacent tissues, contrast agents are used. In
computed tomography two types of contrast media are used, intravenous and
the per os (oral administration).
The first is given from the vein through a venipuncture and offers contouring,
that is, creating contrast between internal organs as well as tissues
of interest while the second outlines the gastrointestinal tract, setting it apart
from the rural structures.
The use of intravenous contrast media makes this possible
angiograms and special diagnostic investigation protocols.
In more detail, CT angiography of the carotid and
vertebral-basal system, brain, thoracic and abdominal aorta, hips
arteries and veins of the lower extremities, angiography of the upper extremities, as well as CT
angiography of pulmonary arteries (pulmonary embolism protocol).
Diagnostic investigation protocols are indicated for liver pathologies,
bile ducts, pancreas, kidneys, adrenal glands as well as for CT urography.
Possible risks of a CT scan?
Computed tomography is a painless and generally safe technique. The risks that
related to computed tomography are due to two main factors:
a) to the patient's exposure to ionizing radiation
Exposure of the patient to radiation can damage the cells and possibly
increase the likelihood of developing a neoplasm in the future. However, this possibility is
small while modern CT systems allow a significant reduction
radiation dose received by the subject. When the examination is sufficiently
reasoned, the benefit of the diagnosis far outweighs the potential
radiation hazard.
b) in the use of contrast agent
Contrast material, although rare, may cause an allergic reaction. Them
more often allergic reactions are mild and appear as a rash or
itch. In very rare cases an allergic reaction can be severe or
even life-threatening. Before each examination, it is important to inform him
doctor if you have had any allergy or other side effect from using contrast material
in the past. The widely used contrast materials used in
CT scans contain iodine.
It is also necessary to inform your doctor if you are pregnant.
CT diagnosis
For the CT diagnosis, it is necessary for the doctor to know in detail the
history of the examinee while it is important to present any previous ones
imaging tests. The CT scan is diagnosed by a medical Radiologist.